
Unit testing is a software testing method where individual components of the software are tested independently to verify each part functions correctly. It's a fundamental practice in software development, aimed at ensuring code quality and reliability by isolating each unit and validating its performance.
The primary objective is to isolate a code section and test its correctness. It helps uncover early bugs and flaws in application code that can be more challenging to identify in the later stages of the software testing life cycle (STLC).

Unit testing is a critical process in software development, where individual components of a program are tested in isolation to ensure they function correctly. This method, primarily performed by developers, focuses on the smallest units of code, like functions or methods, to identify and fix issues early, enhancing overall software quality.
This unit test checks the basic functionality of the multiplication operation, ensuring that the function correctly computes the multiplication of two numbers.
// Function to test function multiplication(a, b) return a * b; > // Unit test for multiplication test('Test the function of multiplication', () => // Setup step const a = 5; const b = 10; // Action step const resultat = multiplication(a, b); // Assert step expect(resultat).toBe(50); >); Unit tests are designed to be run quickly and often — one at a time or all together. They need to be kept simple and clear so that they're easy to read and understand, even if they contain complicated logic or lots of variables. It is run before integration testing; therefore, it can save a lot of time and costs if done correctly. It can be carried out manually or with automated testing tools like Selenium.
Manual unit testing is a process where developers personally write and execute test cases. This method involves creating detailed test plans and offers flexibility and a deep understanding of the code. However, it can be time-consuming and less consistent, especially for larger projects. Manual testing is often preferred for smaller projects or in scenarios where detailed, hands-on examination of code is necessary.
Automated unit testing, in contrast, relies on software tools to execute pre-written tests. It is characterized by its efficiency, consistency, and ability to cover a wide range of test scenarios quickly. Automated tests are ideal for large-scale projects, offering rapid execution and detailed reporting capabilities. This method is particularly effective for regression testing and continuous integration processes.
Unit testing is often considered the first level of web application testing. If you have written a code, you must test it before releasing the software application to ensure it is working as expected.
Therefore, It is required for the following reasons:

Unit testing can be performed by anyone who has access to the source code for the project or application. This includes developers, testers, and QA engineers, although it often involves a combination of these roles. Unit tests should be written by developers who know how a class, function, or module should work. Developers should also know how their code interacts with other systems, such as databases and external systems.
It happens in the development stage, saves developers time, and avoids testing code multiple times. It helps identify issues with the codebase and build and deploy new features confidently. Unit tests make the entire code maintenance easier by ensuring that newly added functionality doesn’t break the existing application’s codebase.
You can even develop new features rather than worrying about the existing code. Unit testing can also be used to shorten the debugging time and assist developers in identifying bugs and flaws in the application before releasing it to the general public.
Benefits that you can’t overlook.
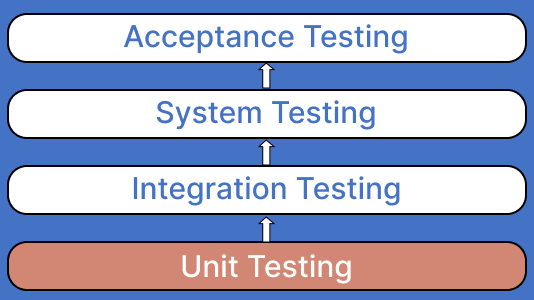
Unit testing is a fundamental part and usually the first stage in the software development life cycle. Here are the six phases of the Unit test life cycle:
It has numerous advantages over the other types of software testing techniques. By running unit tests, developers can get precise feedback and achieve high execution speed. Also, if you run unit tests that validate the functional behavior of an application, and the test fails, in most cases, you can ensure that the issue lies in the function
End-to-end testing and similar testing interact with the application just like a real user does. Therefore, it provides more realistic feedback. Furthermore, unit tests verify how different isolated modules or units function together. However, it can’t validate how these units integrate with other units. In this case, integration testing, end-to-end testing, and similar types of testing can verify how well these units integrate with different units.
By Louise J Gibbs
In a nutshell, the role of Unit testing in QA strategy is to provide fast and early feedback to developers. But you can’t rely entirely on unit tests as they lack some features in a few aspects. Therefore, an ideal approach is to back them with another type of testing in the area where unit tests fall short. Using a test pyramid can be a viable concept as it states that having a larger number of unit tests and fewer other types of tests is good.
The Unit testing techniques can be classified into three parts which help unit testers validate each unit of the application's code in isolation. These techniques fulfill different software requirements and ensure its proper functioning.
The different techniques are:

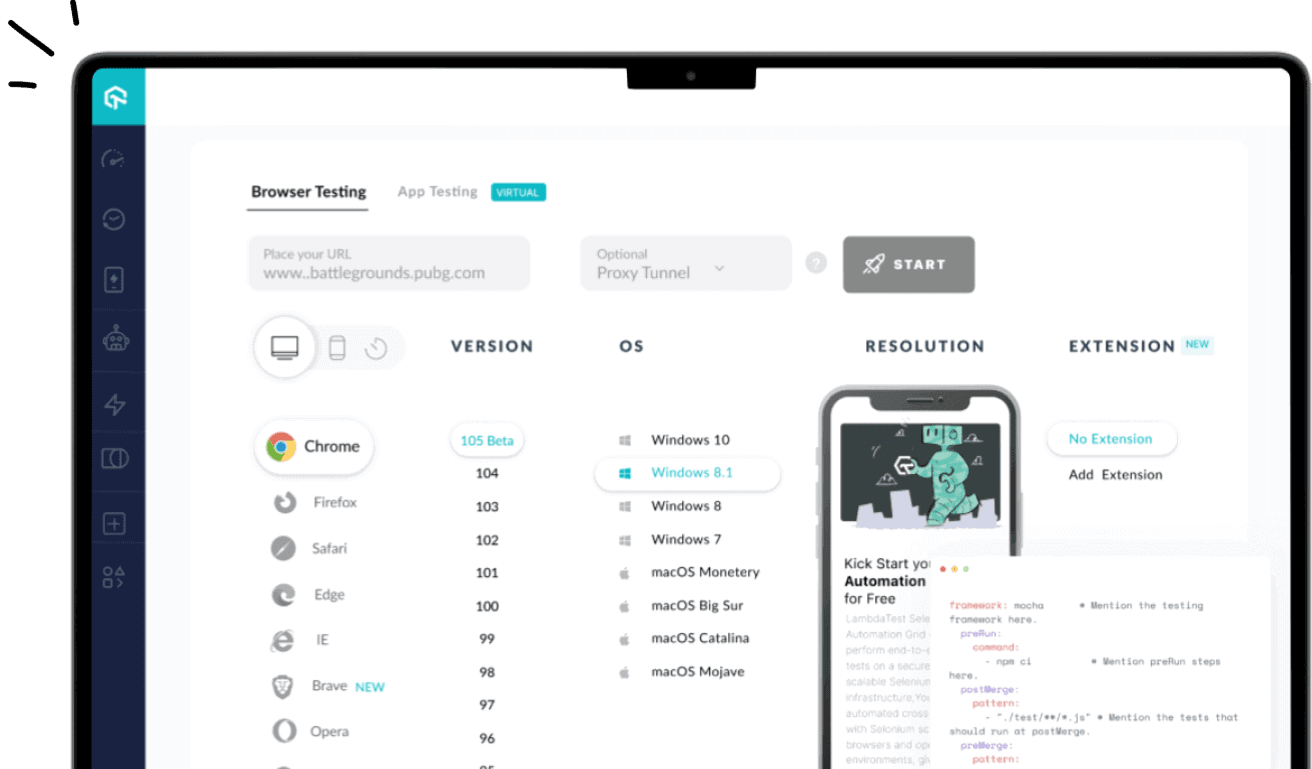
Unit testing forms the foundation for the testing process, preceding integration testing. While integration tests assess the overall functionality of the end product, unit tests concentrate on validating individual components within the software system. Although unit tests may not cover every aspect of the software's functionality, they serve as a swift and efficient method for identifying errors. This rapid execution allows for an increased volume of tests in a shorter span. These tests are typically scripted within a separate testing framework, ensuring their independence from the application itself.
Integration testing is ideal to ensure that all application pieces work together correctly. It involves running your entire application under realistic conditions and ensuring that all components work as expected. This type of testing is often used to ensure that no bugs are introduced when integrating new features into existing applications.
Integration testing is a more comprehensive form of testing that tests both the functionality of your components and their interaction with one another.
Here’s a detailed comparison between Unit and integration testing.
| Unit testing | Integration testing |
|---|---|
| Unit testing focuses on the individual modules of the application. | Integration testing focuses on the combined modules of the application. |
| It is usually the first level of testing but can be performed at any time. | It is performed after Unit testing and before System testing. |
| It can be performed by developers, testers, and QA engineers. | Only performed by testers. |
| It is a white-box testing technique. | It is a black-box testing technique. |
| It can be carried out without the completion of all the parts of the software. | Only be carried out after the completion of all the parts of the software. |
| It is easy to maintain, run and debug. | It’s comparatively high maintenance and slower to run. |
| The issues are easy to find and can be instantly fixed. | The cost of fixing issues is higher and takes longer to resolve. |
| It is limited in scope and may not catch integration errors. | It has a wider scope and may detect system-wide issues. |
| It focuses on module specification. | It focuses on interface specification. |
Earlier, Unit testing of an application was done manually, which was a time-consuming and cumbersome task. However, test automation has made it easier to automate manual approaches to perform test quickly. To automate unit tests, devs and testers leverage some of the best Unit testing frameworks to test the web app’s components.
Here are some of the most widely used and compatible frameworks you can employ for testing individual components.
Why Use Jest? : Ideal for developers working on large JavaScript projects, especially in React, looking for a tool that offers a comprehensive testing solution.
Why Use Jasmine? : Jasmine is ideal for JavaScript testing with its behavior-driven approach, enhancing code readability and maintainability across various environments and tools.
Why Use JUnit? : It's ideal for developers looking for a robust, community-supported framework that seamlessly integrates with Java development workflows.
Why Use TestNG? : Java developers seeking an advanced framework that goes beyond JUnit will find TestNG's extended capabilities highly beneficial.
Why Use PyUnit? : It's Python's default testing framework, offering simplicity and compatibility with the Python ecosystem.
Why Use Pytest? : For Python developers, Pytest offers an intuitive and straightforward approach to both simple and advanced testing needs.
Why Use Mocha? : It's perfect for developers who need a flexible and versatile tool for testing JavaScript applications, especially with asynchronous operations.
Why Use QUnit? : It's particularly well-suited for projects that require a lightweight yet robust testing solution.
Unit tests are fast and easy to write, run, and debug — but that doesn't mean you should skip them altogether. Unit tests can take time to set up, especially if they're not automated, so it's important to find ways to speed up their creation, according to most DevOps principles.
You can perform it in two ways:
However, when you test a website, many issues might be unrevealed related to usability. For example, specific functionality of your website works fine on Chrome 99 (Windows 11) but doesn’t work on Firefox 97 (Windows 11). This makes cross browser testing extremely important to fix such usability issues before your customer finds them.
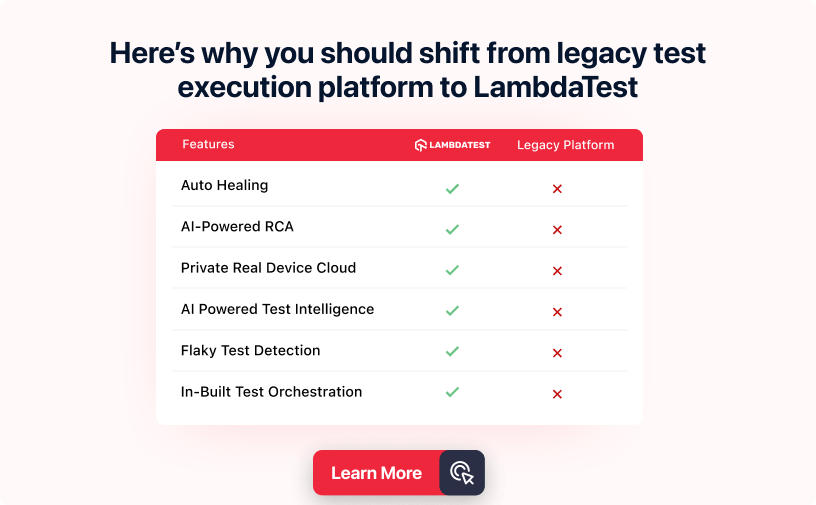
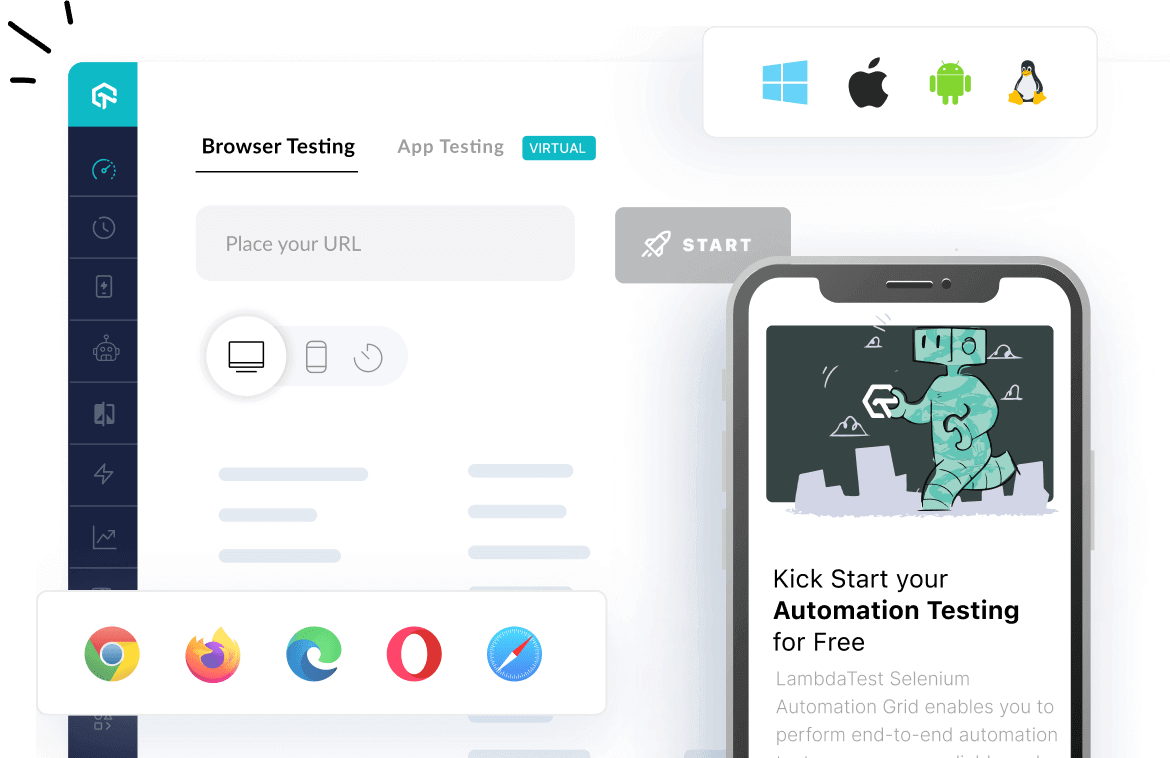
You can utilize various Unit test frameworks to perform automated browser testing and UI testing. A cloud-based testing platform like LambdaTest offers you a scalable cloud to automate your browser and app testing across 3000+ real browsers, devices, and operating systems combinations. It also offers parallel testing to shorten your overall test execution time by multiple folds.
You can subscribe to the LambdaTest YouTube Channel and stay updated with the latest tutorials around automation testing, Cypress UI testing, Responsive testing, and more.
Here are some primary limitations:
Here are a few tips that you can follow to get the most out of Unit testing:
Unit testing is a cornerstone of software development, and it should be part of every developer's toolkit. By creating automated tests for your code, you can ensure that it works properly and will continue to work correctly in the future
If other developers use the software you build, their code will run more smoothly if they know you've already ensured that things will “work as expected.” It keeps bugs from escaping into production, something you don't want as developers or users.
Even better, It isn't as complicated or time-consuming as many believe. And it can be a wonderful learning experience for anyone with a passion for programming who wants to understand their code better.
Delve into our top Unit Testing Interview Questions guide, designed to help you excel in interviews. It covers a wide range of topics, from syntax to advanced techniques, with detailed solutions.
Unit Testing involves validating individual components or modules of a software application. It is carried out during the development phase of an application. It is of two types: manual and automated.
Unit testing is regarded as the first level of testing for validating websites and web applications. Therefore, if you write any code, you must test it before making it live for the general public to ensure they are working as intended.
Unit testing is a software testing technique where individual components or units of code are tested in isolation to ensure they function correctly. It focuses on verifying the behavior of small, independent parts of the software.
To perform unit testing, write test cases that target specific units of code, typically using a unit testing framework like Pytest or JUnit. Execute the test cases, validate the expected behavior, and compare it with the actual output.
Unit testing is essential because it helps detect bugs early in the development process, promotes code quality and maintainability, provides confidence in code changes, and facilitates better collaboration among developers.
In unit testing, a mock is an object that simulates the behavior of a real object or component that the code being tested depends on. Mocks allow you to control and verify interactions with dependencies to isolate and test specific code units.
Unit testing in Python involves using testing frameworks like unittest or pytest to write test cases that verify the functionality of individual units of Python code, such as functions, classes, or modules.
Unit testing is primarily performed by software developers themselves as they write the code. They create test cases to validate the behavior of their code units and ensure they work as expected in isolation before integrating them into larger systems.
Try LambdaTest Now !!
Get 100 minutes of automation test minutes FREE!!
Did you find this page helpful?

Salman works as a Digital Marketing Manager at LambdaTest. With over four years in the software testing domain, he brings a wealth of experience to his role of reviewing blogs, learning hubs, product updates, and documentation write-ups. Holding a Master's degree (M.Tech) in Computer Science, Salman's expertise extends to various areas including web development, software testing (including automation testing and mobile app testing), CSS, and more.

Shahzeb currently holds the position of Senior Product Marketing Manager at LambdaTest and brings a wealth of experience spanning over a decade in Quality Engineering, Security, and E-Learning domains. Over the course of his 3-year tenure at LambdaTest, he actively contributes to the review process of blogs, learning hubs, and product updates. With a Master's degree (M.Tech) in Computer Science and a seasoned expert in the technology domain, he possesses extensive knowledge spanning diverse areas of web development and software testing, including automation testing, DevOps, continuous testing, and beyond.